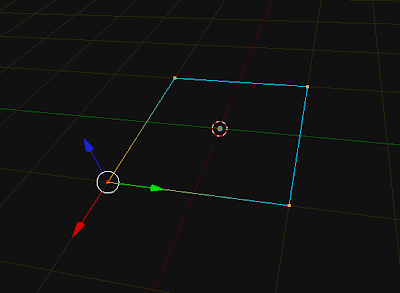
# be in object mode with nothing selected.
import bpy
# create 4 verts, string them together to make 4 edges.
coord1 = (-1.0, 1.0, 0.0)
coord2 = (-1.0, -1.0, 0.0)
coord3 = (1.0, -1.0, 0.0)
coord4 = (1.0, 1.0, 0.0)
Verts = [coord1, coord2, coord3, coord4]
Edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,0]]
profile_mesh = bpy.data.meshes.new("Base_Profile_Data")
profile_mesh.from_pydata(Verts, Edges, [])
profile_mesh.update()
profile_object = bpy.data.objects.new("Base_Profile", profile_mesh)
profile_object.data = profile_mesh # this line is redundant .. it simply overwrites .data
scene = bpy.context.scene
scene.objects.link(profile_object)
profile_object.select = True
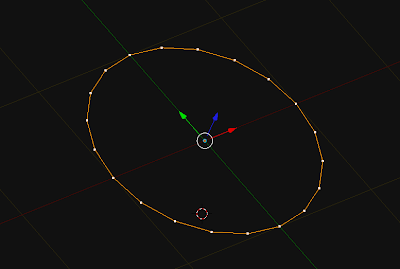
this makes a circle 12 verts, 12 edges. you can modify n_verts ( must be >= 3)
import bpy
import math
from math import sin, cos, radians
# variables
n_verts = 12
profile_radius = 1
section_angle = 360.0 / n_verts
z_float = 0.0
Verts = []
Edges = []
for i in range(n_verts):
x_float = sin(math.radians(section_angle*i))
y_float = cos(math.radians(section_angle*i))
Verts.append((x_float, y_float, z_float))
for i in range(n_verts):
if i == n_verts-1:
Edges.append([i, 0])
break
Edges.append([i, i+1])
profile_mesh = bpy.data.meshes.new("Base_Profile_Data")
profile_mesh.from_pydata(Verts, Edges, [])
profile_mesh.update()
profile_object = bpy.data.objects.new("Base_Profile", profile_mesh)
profile_object.data = profile_mesh
scene = bpy.context.scene
scene.objects.link(profile_object)
profile_object.select = True

here's a version using Euler, Vector, Vector.rotate, and math.radians
import bpy
import math
from math import radians, pi
from mathutils import Vector, Euler
# variables
n_verts = 20
profile_radius = 1
section_angle = 360.0 / n_verts
z_float = 0.0
Verts = []
Edges = []
'''
>>> m = Vector((1.0, 0.0, 0.0))
>>> eul = Euler((0.0, 0.0, math.pi), 'XYZ')
>>> m.rotate(eul)
'''
ampline = Vector((1.0, 0.0, 0.0))
for i in range(n_verts):
x_float = ampline.x
y_float = ampline.y
rad_angle = math.radians(section_angle)
myEuler = Euler((0.0, 0.0, rad_angle),'XYZ')
# changes the vector in place and is accumulative
ampline.rotate(myEuler)
Verts.append((x_float, y_float, z_float))
for i in range(n_verts):
if i == n_verts-1:
Edges.append([i, 0])
break
Edges.append([i, i+1])
profile_mesh = bpy.data.meshes.new("Base_Profile_Data")
profile_mesh.from_pydata(Verts, Edges, [])
profile_mesh.update()
profile_object = bpy.data.objects.new("Base_Profile", profile_mesh)
profile_object.data = profile_mesh
scene = bpy.context.scene
scene.objects.link(profile_object)
profile_object.select = True
a slight variant of the above for loop in range, allows you to change the diameter as a function of the position on the circumference. This replaces lines 20-30 from the previous snippet
for i in range(n_verts):
ampline = Vector((1.0, 0.0, 0.0))
rad_angle = math.radians(section_angle*i)
myEuler = Euler((0.0, 0.0, rad_angle),'XYZ')
ampline.rotate(myEuler)
x_float = ampline.x
y_float = ampline.y
Verts.append((x_float, y_float, z_float))